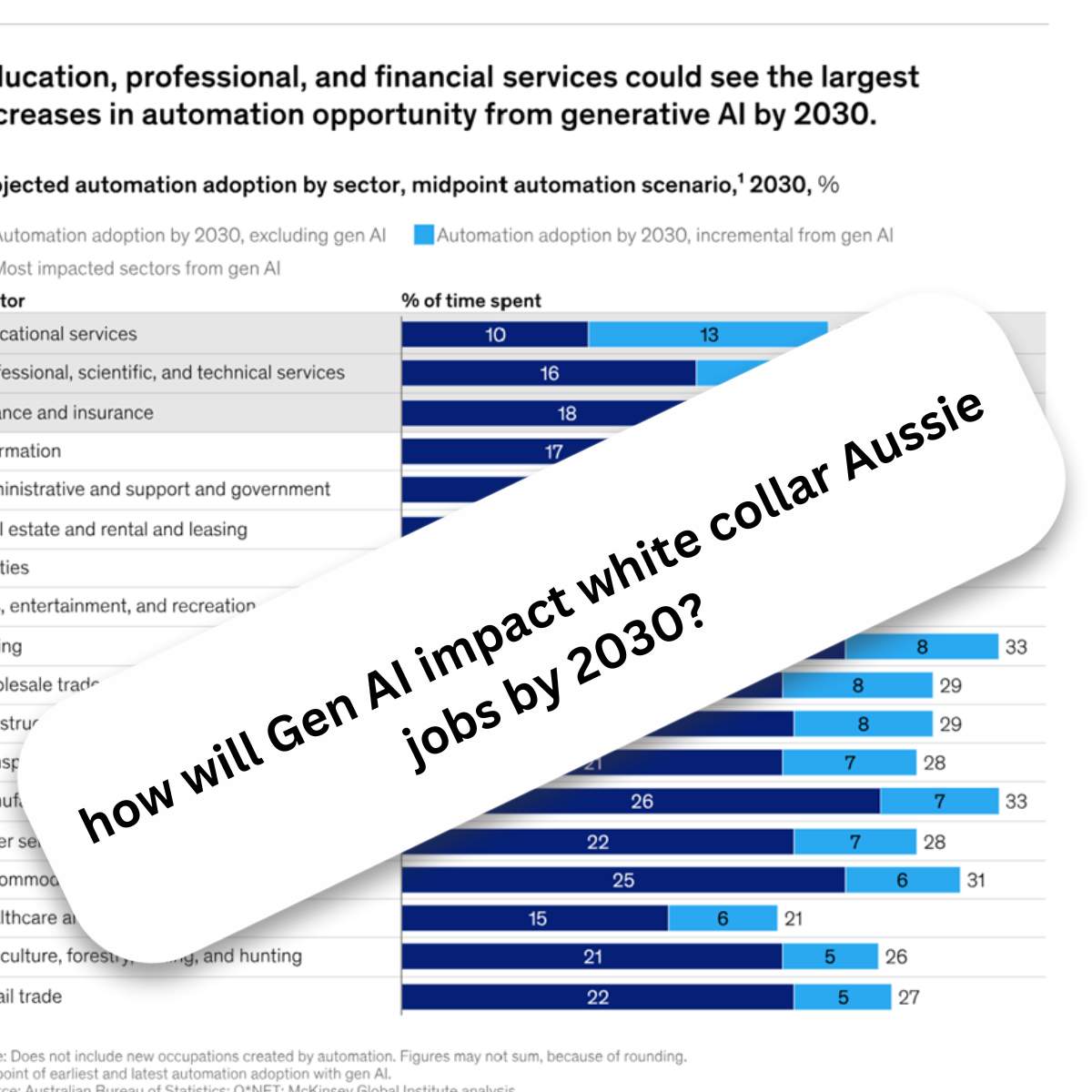
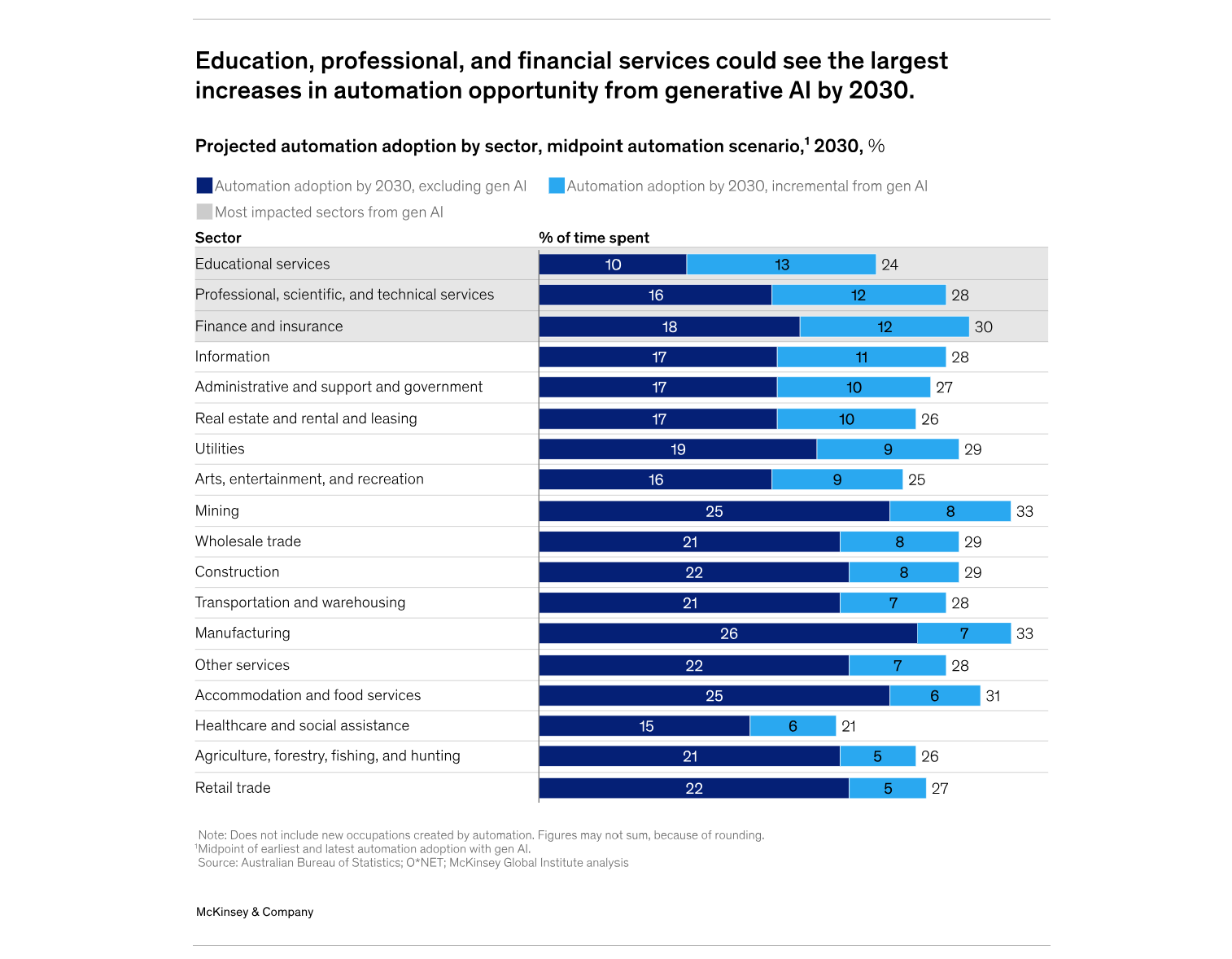
The impact of Gen AI on Aussie jobs by 2030
For the first time in history, the workforce will be one of hybrid intelligences – the coming together of human and machine intelligence – with a new challenge to make that relationship productive and trusted [1]
However throughout history, one constant remains—our inventiveness. Whether it's developing new technologies or finding creative solutions to problems, humans have always displayed a remarkable ability to innovate. This spirit of inventiveness is crucial as we continue to adapt to the changing landscape.
Four key areas of change
1 Occupation Changes: The introduction of generative AI is expected to bring about changes in the demand for different occupations. By 2030, it is estimated that one-tenth of Australian workers could see more than 40% of their task hours automated, while two-thirds of workers could see 20% to 40% of their task hours automated. This could result in approximately 1.3 million workers needing to transition into different lines of work by 2030.
2 Wage and Education Impact: The impact of generative AI on occupations varies across different wage quintiles. Occupations in the highest wage quintile may see their automation adoption increase by 1.8 times due to generative AI, compared to 1.2 times for the lowest wage quintile. Additionally, workers with lower levels of formal education and women are more likely to be displaced and need to change occupations.
3 Reskilling Opportunities: As the work landscape changes, there will be a need for workers to upskill and transition into new roles. Skill building and continuous learning will become crucial for navigating the future work landscape. There will be an increased demand for skills involving social and emotional intelligence, as well as technological skills such as engineering and digital literacy.
4 Sector-specific Impact: Generative AI is expected to have different impacts across sectors. In retail trade, it could introduce greater personalisation and improve inventory management and customer service. In financial services and insurance, it could reshape risk assessments, fraud detection, and customer service. In the public sector, it could transform activities such as education delivery, citizen interactions, and financial analysis.
Generative AI has the potential to assist with a wide range of tasks across various industries.
Seven examples of tasks that gen AI can augment
1 Writing and Content Creation: Gen AI can help generate written content, such as articles, reports, and blog posts. It can assist with writing marketing copy, social media posts, and email newsletters. This can save time for content creators and marketers, allowing them to focus on other aspects of their work.
2 Design and Creativity: Gen AI can be used to generate designs for products, logos, websites, and user interfaces. It can assist with creating visual content, such as graphics, illustrations, and animations. This can be particularly useful for designers and creative professionals who can leverage gen AI to generate ideas and prototypes.
3 Data Analysis and Insights: Gen AI can analyse large datasets and provide insights and recommendations based on the data. It can assist with data cleaning, data visualisation, and predictive analytics. This can help businesses make data-driven decisions and identify patterns and trends in their data.
4 Customer Service and Support: Gen AI can be used to develop chatbots and virtual assistants that can interact with customers and provide support. It can understand natural language and respond to customer inquiries, troubleshoot issues, and provide relevant information. This can improve customer service efficiency and provide 24/7 support.
5 Legal and Compliance: Gen AI can assist with analysing legal documents, contracts, and regulations. It can help identify relevant information, highlight potential risks, and provide recommendations. This can be valuable for legal professionals and organisations dealing with large volumes of legal documentation.
6 Scientific Research and Discovery: Gen AI can assist scientists and researchers in analysing complex data, conducting simulations, and generating hypotheses. It can help accelerate scientific discovery by processing and interpreting large amounts of data, identifying patterns, and suggesting new avenues for research.
7 Operations and Process Optimisation: Gen AI can assist with optimising business processes, supply chain management, and logistics. It can analyse data to identify inefficiencies, recommend process improvements, and automate repetitive tasks. This can lead to increased operational efficiency and cost savings.
It is important to note that while gen AI can assist with these tasks, it is currently more focused on task augmentation rather than outright job automation. Human involvement and oversight are still necessary in many cases to ensure accuracy, ethical considerations, and decision-making.
For instance, in this recent Forbes article [4] we note the author sees that not all white-collar roles are at risk of being replaced by automation.
- Jobs relying on human interaction and emotional intelligence, such as therapists, counselors, social workers, and teachers, are resistant to AI replacement
- High-level white-collar roles involving complex decision-making are secure from automation
- Customer-facing positions like salespeople remain safe due to the need for building and maintaining client relationships
- Management consultants have future-proof careers due to high levels of human interaction and problem-solving required
- Lawyers depend on the human touch in their work but can use AI to assist with reviewing legal documents efficiently
- AI can handle some human resources tasks but resolving conflicts and managing employee relations still require human interpersonal skills.
To continue our opening quote:
These hybrid teams will have a multitude of skillsets. Technical skills in data science, health and engineering can build what may be needed, while human skills like human-centric design and frontline change management will make those services both relevant and successful. That implies a balance of abilities that are nurtured from both STEM and humanities education. Our technical specialists need to learn from the humanities how different people have different perspectives that need to be integrated; and our social scientists need the mathematical literacy and critical thinking skills that STEM can bring, a creative awareness of the skills needed to solve problems and the tools that the data and traditional sciences have to draw on.[2]
Humans and AI will work together and humans will adapt.
While it may lead to job displacement and the need for occupational transitions, it also presents opportunities for upskilling, higher-wage jobs, and increased productivity. Strategic action by employers, governments, and educators will be crucial in harnessing the benefits of generative AI and ensuring a smooth transition for workers. The ethical, social imperative is to ensure that workers most at risk of being displaced by AI – those in easily automated roles, are supported to upskill and transition successfully.
History is filled with stories of change, evolution, and human resilience. From the Industrial Revolution to today's tech-driven world, humanity has repeatedly demonstrated its ability to ad apt and thrive in the face of new challenges. For everyone in the workforce today facing the challenges and opportunities of AI, understanding our past can inspire confidence in navigating the present and future.
As career professionals we would advise you to keep informed about AI advances in your industry and profession, stay alert to opportunities and be prepared to update your career blueprint and learn and re-skill as needed.
Humanity has successfully transitioned through significant change before—and we'll do it again – and hopefully with sufficient empathy, insight and critical thinking.
Endnotes
References